The Art of Project Management: Exploring Key Types and Strategies

Comments are closed.

In the ever-evolving landscape of business and technology, project management is the art that brings vision to life. It’s not just about organizing tasks; it’s about ensuring that goals are achieved, resources are optimized, and teams work in harmony. This blog will explore the key types of project management strategies and offer guidance on how to choose the right one for your needs.
“The way to get started is to quit talking and begin doing.” – Walt Disney
At its essence, project management involves planning, executing, and monitoring a series of tasks to achieve a specific objective. Unlike regular operations, projects are temporary endeavors with a clear start and finish.
Effective project management requires balancing three critical elements:
Scope: Defining what the project will deliver.
Time: Setting deadlines and milestones.
Cost: Managing the budget efficiently.

These elements form the foundation of what is often referred to as the project management triangle, where altering one factor typically impacts the others.
Here’s an overview of the most prominent project management methodologies, each with unique strengths:

1. Waterfall Methodology
The Waterfall approach follows a linear, sequential process, where each phase—from initiation to closure—is completed before the next begins. It’s ideal for projects with clearly defined requirements, such as construction or large-scale infrastructure.
Why Choose Waterfall?
Predictable and structured
Works well for fixed-scope projects
2. Agile Methodology
Agile thrives in environments requiring flexibility and adaptability. It breaks projects into smaller units called sprints, delivering incremental value. Agile is especially popular in software development and industries experiencing rapid change.
Why Choose Agile?
Highly adaptable to change
Encourages collaboration and feedback


3. Scrum Framework
Scrum is a subset of Agile, emphasizing teamwork and iterative progress. With defined roles like Scrum Master and Product Owner, it’s ideal for dynamic projects with evolving requirements.
Why Choose Scrum?
Short, focused sprints
Regular reviews to ensure alignment
4. Kanban Methodology
Kanban uses visual boards to manage workflows and prioritize tasks. It’s well-suited for ongoing processes like maintenance or service delivery.
Why Choose Kanban?
Visual task management
Continuous delivery and prioritization

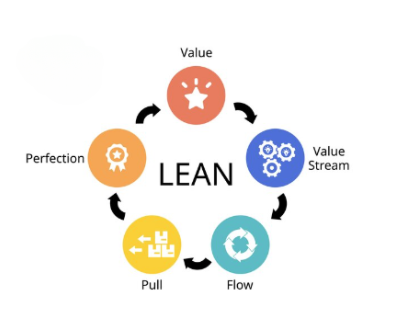
5. Lean Project Management
Lean focuses on delivering maximum value while minimizing waste. Initially rooted in manufacturing, it’s now widely applied in various industries, including software.
Why Choose Lean?
Efficiency-driven
Prioritizes customer value
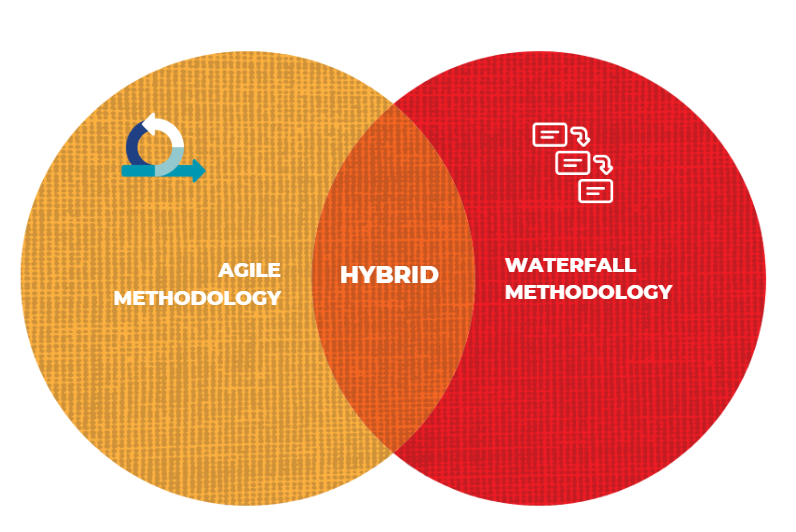
6. Hybrid Methodology
Hybrid combines elements of Waterfall and Agile, offering a balanced approach. It’s perfect for projects with both predictable and flexible components.
Why Choose Hybrid?
Versatility
Customizable for diverse needs

7. Critical Path Method (CPM)
CPM identifies the longest sequence of dependent tasks and focuses on ensuring their timely completion. It’s commonly used in construction and engineering projects.
Why Choose CPM?
Highlights critical tasks
Optimizes timelines
8. Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at eliminating defects and improving quality. It’s best suited for precision-focused projects in manufacturing or healthcare.
Why Choose Six Sigma?
Emphasizes quality and process optimization
Data-centric decision-making


Selecting the right methodology depends on several factors:
Project Scope and Complexity: Agile works well for complex projects with evolving requirements, while Waterfall is better for straightforward projects.
Team Dynamics: Small, collaborative teams may thrive under Agile, while larger, hierarchical teams may prefer Waterfall.
Industry: Lean and Six Sigma are ideal for manufacturing, whereas software development often benefits from Agile or Scrum.
Stakeholder Involvement: Agile and Scrum are excellent for projects requiring frequent stakeholder input.
Timeline and Budget: For tight deadlines and budgets, CPM or Hybrid approaches may be more effective.
The art of project management lies in understanding your project’s unique needs and aligning them with the right strategy. Whether you choose the structured path of Waterfall, the adaptability of Agile, or the efficiency of Lean, the key is to remain focused on your goals while staying flexible enough to adapt to challenges. By mastering these methodologies, you can ensure your projects not only meet expectations but exceed them.